Run flempar on any system with Docker
By Niek Tettero, Frederik Heylen
TLDR
Run flempar on an any system, without having to download R or Rstudio with two simple commands:
docker pull datamarinier/flempar
docker run --rm -ti -e PASSWORD=yourpassword -p 8787:8787 datamarinier/flempar
For whom is this blog?
This blog is for anyone who would like to use the flempar package without having to download all the dependencies on their machine. This can be achieved by using Docker and running only two simple commands.
Docker is a tool that allows users to deploy and run applications securely and efficiently by using ‘containers’. These containers contain everything for an application to work, such as the software, libraries, and other dependencies. As a result, these containers run the same way on any machine, avoiding compatibility issues. For our application, Docker allows you to run an RStudio session in your browser. So you don’t even need to download R or Rstudio to run this solution. We installed the proper packages and dependencies so you can get started using flempar immediately.
Docker containers are a powerful tool for creating reproducible and portable software environments, making them an ideal choice for conducting scientific work.
I will guide you through the process of installing Docker and running a container. For advanced users, I’ll also show you how to create a custom image that includes any necessary software, dependencies, or packages. This is useful if you want to deploy flempar on a virtual machine in the cloud, for instance when extracting large amounts of data.
Prerequisites
To get started, first install Docker. Go to https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/ and follow the instructions. The general steps are:
- Download the Docker installer from the Docker website. Note that there are different installers for Windows, Mac, and Linux.
- Run the installer and follow the prompts to install Docker.
- Once the installation is complete, you can open the Docker Desktop app to start using Docker.
You do not need any experience with Docker or any other software. Following this blog should be enough to get you started. If you experience any problems with installing Docker, please refer to the original documentation.
Docker hub
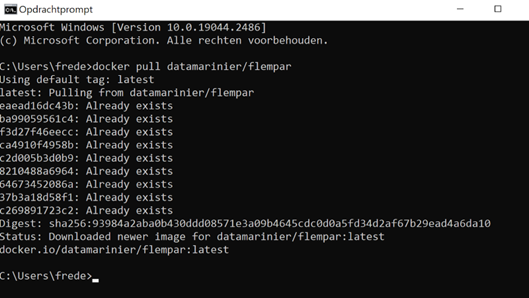
To get started immediately, you can pull the image from Docker Hub. You can do this by opening a terminal. In Windows you can do this by typing CMD in the menu’s search bar. To open a terminal on Mac, go to the launchpad and search for terminal, or search ‘terminal’ in the spotlight search bar, which you can open with ⌘ + space. In the terminal, run:
docker pull datamarinier/flempar
In this case, the following command will download the latest version of the flempar image.
Running containers
You can run the container by running the following command in your terminal.
docker run --rm -ti -e PASSWORD=yourpassword -p 8787:8787 datamarinier/flempar
Now your container is running, you can access it through your browser. Type localhost:8787 in your browser to gain access. The username stays the same (rstudio), but the password is now set to the password you specified in the command.
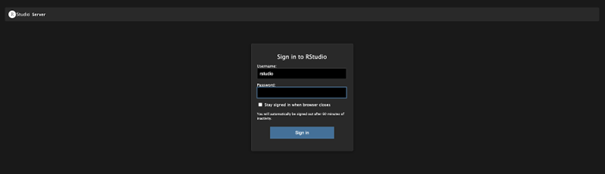
Now paste in the console:
library(flempar)
getmp()
To avoid using excessive system resources, stop the container once you are done. This can also be done via the terminal.
First run the command below. This will give you a list with all the containers that are running.
docker ps
Use the docker stop command followed by the container ID or name to stop the container.
docker stop <name or id>
Building the image - advanced
It could be that you would like to perform additional analyses using other software or other packages. More advanced users who wish to adapt this Docker container can build a new image, using the flempar base image. For instance, adding other R libraries, or Python to your image.
Building a Docker image takes a few simple steps. First, create a file called Dockerfile in your project directory (without an extension). Secondly, specify the base layer using the FROM instruction at the beginning of your Dockerfile (in this case datamarinier/flempar). Thirdly, add the necessary instructions to install the new software on top of the base layer. In the example below we add the R package reticulate. Lastly, set the ENTRYPOINT or CMD instruction to specify the default command to run when the container starts.
FROM datamarinier/flempar
RUN install2.r -e \
-r 'http://cran.rstudio.com' \
reticulate && rm -rf /tmp/downloaded_packages
CMD ["/init"]
When all instructions are written in your Dockerfile, open a terminal window and navigate to the project directory. Once in the directory, run the command below.
docker build -t 'image name' .
Note the ‘.’ at the end of the command. It tells the docker to use the current directory. If the instructions and commands are specified correctly, you have now built a Docker Image that can be used to create containers.